Dear EarthTalk: Can we do a better job repurposing outdated technology instead of trashing it?
—R.T Smith, via e-mail
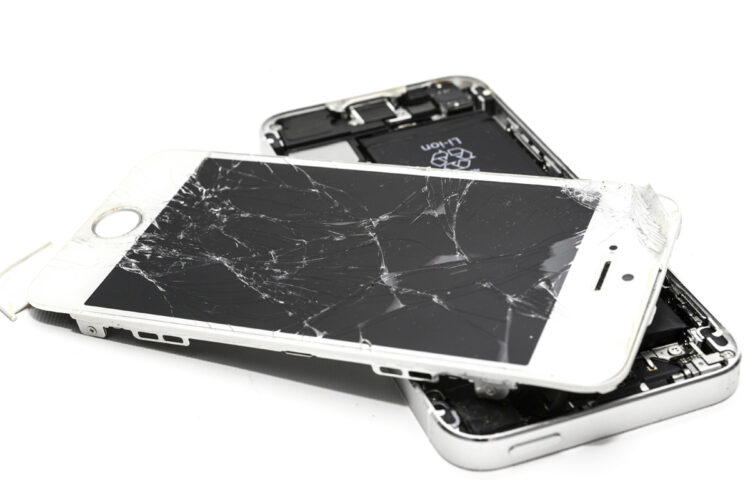
March 21. The annual production of “e-waste”—electronic products that have reached the end of their useful life and tossed—is rising by 2.6 million tons globally, on track to reach 82 million tons by 2030. While recycling is often viewed as the best solution for managing e-waste, it is a complex and costly requiring substantial resources, specialized equipment, and energy to process hazardous materials.
A more sensible alternative is repurposing the technology through practices like IT Asset Disposition. By refurbishing devices, we can conserve resources and achieve financial savings—all while extending the lifespan of technology.
Repurposing advantages
Repurposing technology preserves critical materials like minerals and metals, otherwise often extracted at a significant environmental cost. Redistributing components within a company instead of making new ones saves time and resources—and extends hardware life. “The more metals we recycle, the fewer have to be mined,” says Kees Baldé, senior scientific specialist at the UN Institute for Training and Research.
Dell, HP, Microsoft, Apple, Lenovo, Cisco, Google, Amazon and Sony all have programs to take back and find new homes for outdated tech hardware. Also, TechSoup, Good360 and Computers with Causes are non-profits which specialize in redistributing refurbished tech to charitable organizations.
Waste stream
E-waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams, yet less than a quarter is properly recycled. E-waste contains substances like lead, mercury and cadmium, which can leach into soil and water supplies and are linked to neurological, respiratory and developmental disorders, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Beyond environmental advantages, repurposing technology saves money by selling or trading in old devices through eBay or manufacturer trade-in programs. Leasing arrangements also provide access to updated technology sans frequent disposal. With creativity, you can DIY old devices into something completely new, like a tablet into a digital recipe book or an old laptop into a home media server.
The EU’s “Right-to-Repair” laws highlight this trend.
Quotable
“We expect Council to adopt their position soon, so we can begin negotiations to transform these measures into law and pave the way for a truly circular European economy,” European Parliament member Rene Repasi shares.
With less than a quarter of e-waste recycled properly globally, adopting a thrifty mindset can drive real change. As a consumer, choose to donate or repurpose outdated devices can conserve resources, save money, and reduce environmental impact. In our technology-dependent world, this shift isn’t simply beneficial—it’s essential.
CONTACT: Electronic Waste Rising Five Times Faster than Documented E-waste Recycling, https://ewastemonitor.info/the-global-e-waste-monitor-2024/.
EarthTalk® is produced by Roddy Scheer & Doug Moss for the 501(c)3 nonprofit EarthTalk. See more at https://emagazine.com. To donate, visit https://earthtalk.org. Send questions to: question@earthtalk.org.